Project Title: Illinois State University: Solid Waste Characterization and Opportunity Assessment of the Bone Student Center
Sectors: Higher Education, Caterers, Food Service, Retail
Location: Normal, IL
Services: Implementation Assistance, Stakeholder Engagement, Fostering Sustainable Behavior, Waste Characterization/Reduction/Management
Background: In June 2022, Illinois State University (ISU) completed the University’s first-ever Sustainability Strategic Plan. Among the many topics covered in the plan, “Materials Management and Waste Reduction” was a key focus. Soon after the release of the report, the Illinois Sustainable Technology Center (ISTC) Technical Assistance Program (TAP) reached out to the ISU Director of Sustainability, Elisabeth Reed, to discuss opportunities for support and collaboration. After several discussions, it was decided that ISTC would conduct a waste characterization study (waste audit) to collect, sort, and weigh waste and recycling samples and identify opportunities for waste reduction and diversion. The Bone Student Center’s variety of uses and activities made it a good representation of the types of waste generated across the ISU campus.
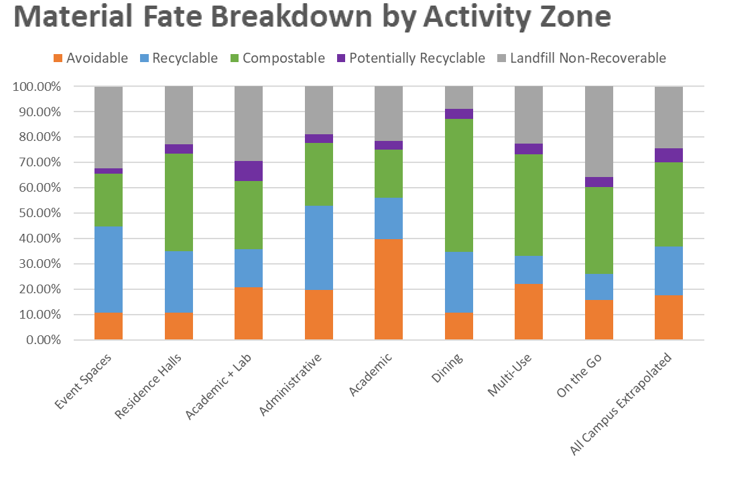
Approach: Beginning in June 2023, ISTC began meeting with the ISU team to better understand the various areas and activities of Bone Student Center along with discussing the logistics of collecting and sorting waste and recycling samples. It was determined that ISTC, along with ISU volunteers, would collect waste and recycling samples from three “activity zones” of the Bone Student Center:
- Catering – This included one kitchen and one dishwashing room used by both catering staff and retail outlets.
- Retail – This encompassed food service locations as well as some indoor and outdoor seating locations used by customers.
- Concourse & Office – This encompassed general hallways, lounge and study spaces, event halls, one classroom, and office spaces.
The physical collection, sorting, and weighing of material took place on September 26-27th, 2023 in the Visitor parking lot of the Bone Student Center on the ISU campus. As per the ASTM D5231 standard for processing solid waste, we aim for 200-pound samples of both landfill-bound trash and single-stream recycling.
The TAP team also conducted a walkthrough of the Bone Student Center, taking pictures, observing current waste management practices, and conducting informal stakeholder engagement in each of the three activity zones.
The resulting report, presented to ISU staff in December 2023, describes and visualizes our findings from this data. An Opportunity Assessment included within that report details strategies and recommendations to reduce overall waste generation and divert additional materials from the landfill in each of the three activity zones, categorized as:
- Education (e.g., Develop standardized educational signage for all single-stream recycling bins.)
- Collection Container Improvement (e.g., Ensure trash and recycling bins are co-located to make recycling more convenient for building occupants.)
- Programs & Procedures (e.g., Target single-use plastics or plastics not accepted in single-stream recycling bins.)
Results: Through this waste characterization study, the TAP team collected data that will inform ISU’s commitment to their Sustainable Strategic Directions of Food and Events as well as Materials Management and Waste Reduction.
“The waste characterization study conducted by the Illinois Sustainable Technology Center provided valuable data that will guide us towards more sustainable practices within our student center and throughout our campus. The knowledge and expertise of the ISTC team elevated our understanding of various waste streams and provided realistic solutions towards diversion and waste reduction.” — Elisabeth Reed, ISU Director of Sustainability
Other projects with this client: None at this time.





 Project Title: University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC) Integrated Solid Waste Management Plan
Project Title: University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC) Integrated Solid Waste Management Plan