Project Title: Materials Management Advisory Committee Report to the General Assembly
Sector: State Government
Location: Illinois, Statewide
Service(s): Sustainability Planning, Stakeholder Engagement, Resilient Solutions
Background: In July 2019, Governor Pritzker signed House Bill 3068, which created the Statewide Materials Management Advisory Committee (MMAC). Coordinated by the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and comprised of a wide variety of recycling, composting, materials management, and solid waste professionals, the Committee was charged with investigating current recycling and solid waste practices and recommending options to the Illinois General Assembly to divert wastes from Illinois landfills. These recommendations were also meant to include improvements to the form and contents of county waste management plan required by Illinois law.
Shantanu Pai of the ISTC Technical Assistance Program (TAP) served as co-chair (along with Suzanne Boring of the Illinois EPA) for the MMAC Measurement Subcommittee. Additional subcommittees existed for education and outreach, infrastructure development, market development, and local government support. Though not official members of the MMAC or its subcommittees, TAP staff members Savannah Feher, April Janssen Mahajan, and Joy Scrogum provided support to the measurement subcommittee and to the overall efforts of the MMAC and Illinois EPA coordinating team for the achievement of the MMAC goals.
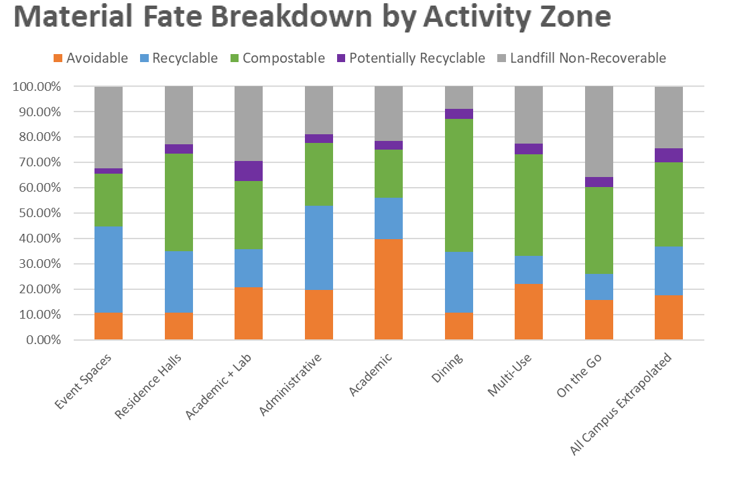
Approach: The primary purpose of the Measurement Subcommittee was to identify, capture, and evaluate existing data reflecting the state of waste and materials management in Illinois in 2018, the base year for the reported data. Using those data, the Measurement Subcommittee was tasked with developing a matrix reflecting the environmental impacts of diverting specific materials from landfills and relaying that information to the entire Committee. This data was gathered through multiple efforts, including a statewide survey sent to all Illinois counties to gather information about solid waste planning, reporting, and programs across the state, as well as outreach to all documented waste infrastructure sites across the state (including transfer stations and collection sites for landfill-bound, recyclable and compostable materials) to verify site status and details. This infrastructure information was then used to create interactive maps that allow users to access accurate and up-to-date information regarding disposal options near them.
The overall MMAC findings, along with the associated recommendations from various subcommittees, were compiled in report form and submitted to the 102nd General Assembly on July 1, 2021.
Results: The full MMAC report submitted to the Illinois General Assembly is available online at https://www2.illinois.gov/epa/topics/waste-management/materials-management/Documents/MMAC_Report_Approved_7_1.pdf.
An ISTC blog post provided an overview of this effort.
Monitor the Illinois General Assembly website and the Illinois EPA Materials Management pages for future updates. See also the recorded Illinois Recycling Association/Illinois Recycling Foundation webinar from April 2021 in which provided an overview of the MMAC draft recommendations at that time.
Other Projects with this Client (Illinois EPA): https://tap.istc.illinois.edu/category/illinois-environmental-protection-agency-epa/







 Project Title: University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC) Integrated Solid Waste Management Plan
Project Title: University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC) Integrated Solid Waste Management Plan